The Threat Indicators dashboard displays information about such anomalous file activity on active client computers and in backup jobs. This dashboard provides a single location for identifying this activity, and allows you to act on potential threats with quick and safe recovery options, as follows:
-
View file path information for the file anomalies and track anomaly trending information.
-
Recover the most recent good versions of files.
-
Recover the entire client computer as a virtual machine.
Commvault bases its file anomaly thresholds on historical activity and machine-learning algorithms, which separate false positives from typical activity on the file system.
You can configure the alerts when anomalous activities are detected. For more information, see File Activity Anomaly Alert.
Note
-
File anomalies that are older than 7 days are pruned automatically.
-
When a file system is installed on a VSA client that has backup anomaly enabled, then the backup that has the latest anomalous job will be listed on the dashboard.
The Threat Indicators dashboard also displays anomalies in the file types of backed up files on Windows client computers. The anomaly is displayed when there is a mismatch in the file type of the file and the file extension. To enable anomaly check on file types, add the DetectMimeType additional setting with value 1 on the client computer.
Note
-
To view the Threat Indicators dashboard, both the client and the CommServe computer need to be at Feature Release 11.23 or later.
-
The Threat Indicators dashboard is available to tenant administrators as well as to users who have the necessary permissions on the client computer with the anomaly.
-
To view the file grid information on the Threat analysis details page, the user must have browse permissions. Otherwise the user can view only the graph and not the file grid with the affected files and their paths.
What Is Monitored
-
Unusual activity on the file system (Windows clients only).
-
Unusual activity in backup jobs (Windows and Linux clients, virtual machines, and network shares).
-
Unusual activity in backup file sizes (Windows and Linux clients, and virtual machines).
-
Unusual file data-related activity (Windows clients only).
-
Mismatches in the file type and file extension of the backed up files (backup jobs that utilize V2 indexing).
Procedure
-
From the navigation pane in the Command Center, click Monitoring > Threat Indicators.
The Threat Indicators dashboard appears, as follows:
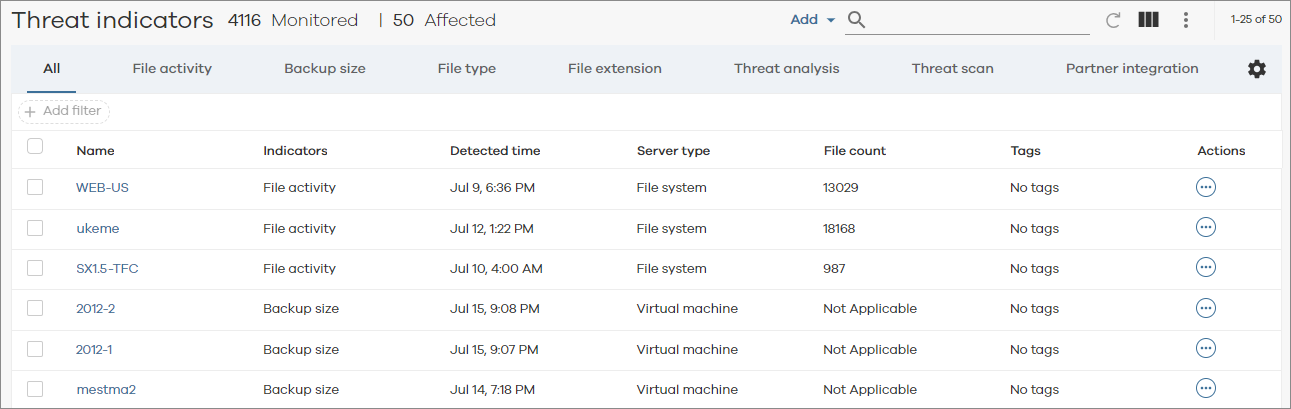
-
To view clients listed by type of anomaly, and then to act on potential threats with recovery options, click the following tabs:
-
File activity. File-related anomalies such as the creation or deletion of a large number of files, as well as backup file-related anomalies such as when the number of created, deleted, or modified files in a backup job changes abruptly from the normal behavior.
For more information, see File Activity Anomalies.
-
Backup size. Anomalies in the amount of data written to media during backups of file systems and virtual clients.
For more information, see Backup Size Anomalies.
-
File type. Anomalies related to mismatches in file type metadata and file extensions, which can suggest the presence of a malware attack.
For more information, see File Type Anomalies.
-
File extension. Anomalies related to backed up files with specific extensions, which can suggest the presence of a ransomware attack.
For more information, see File Extension Anomalies.
-
Threat Analysis. Anomalies related to the number of versions of files, which can suggest that files are encrypted or corrupted by malware.
For more information, see Threat Analysis.
-
Threat Scan. Analysis of backup files for high levels of entropy and change, which can indicate ransomware and/or malware infections within backup data.
For more information, see Threat Scan.
-
Partner Integration. Anomalies generated via third-party security and monitoring platforms. These partner integrations offer insights regarding various cybersecurity threats and vulnerabilities.
For more information, see Partner Integration.
-