Cloned client cannot register with CommServe host
Two client computers with the same name cannot coexist on the same CommServe instance. When a client computer is cloned, the clone must be renamed.
For more information, see the following troubleshooting article: Cloned Client cannot Communicate with CommServe Host.
CommCell components cannot communicate through a VPN tunnel
For more information, see the following troubleshooting article: CommCell Components Not Communicating through VPN.
Communication errors after changing existing network configurations
Problem
After making changes to the existing firewall configuration of a client computer, communication errors occur.
Solution 1
Perform the following steps to avoid communication errors:
-
From the CommCell Console, right-click the client computer, click All Tasks, and then click Push Network Configuration.
-
Right-click the MediaAgent or proxy computer, click All Tasks, and then click Push Network Configuration. Repeat this step for all applicable MediaAgents.
-
Right-click a CommServe computer, click All Tasks, and then click Push Network Configuration. Repeat this step for all applicable client computers and client groups.
Solution 2
If you change the incoming ports of a client computer that is already configured with network settings, you may need to restart the client services for the new configuration to take effect.
For more information, see Services - Getting Started.
Solutions 3
You can also run the cvfwc_ping command to test connectivity to the client computer. For more information, see Firewall Connectivity Test Tool.
Connectivity loss between CommServe computer and client during network configuration
Problem 1
While configuring the network for a client computer or client group, connectivity between the CommServe computer and the client or client group being configured may be lost.
Solution
If Push Network Configuration fails to update the client, and returns a communication error, complete the following steps to update the client computer or client group's new network configuration:
-
From the CommCell Console, right-click the client computer you just configured, and then click Properties.
-
From the Network Route Configuration tab, click the Summary tab, and then copy its contents to the FwConfig.txt file located in the <software installation path>/Base folder.
Note
Recent changes to the network configuration of a client computer are reflected in the Summary tab. Unless you use Push Network Configuration, the client will not be updated with the latest changes.
Problem 2
When you change the name of a client computer, connectivity between the client and the CommServe computer may be lost.
Solution 1
After performing the name change on the client, right-click the client computer from the CommCell Browser, click All Tasks, and then click Push Network Configuration.
Solution 2
Run the cvfwc_ping command to connect to the client computer. For more information, see Firewall Connectivity Test Tool.
Firewall Rules for Deconfigured Clients are Automatically Deleted
During a feature release upgrade, firewall rules for deconfigured clients are automatically deleted from the CommServe database.
For more information, see the following troubleshooting article: Firewall Rules for Deconfigured Clients are Automatically Deleted.
Logging in to a CommCell Console times out
Logging in to a CommCell Console (remote or web-based) may time out if it was set up to connect through a firewall, but the firewall's configuration has changed.
For more information, see the following troubleshooting article: Timeout when Attempting to Log in to CommCell Console.
Troubleshooting network transfer rates on a computer
You can use the nSTATS_MEASURE_INTERVAL additional setting and the nSTATS_LOG_INTERVAL addition setting to help troubleshoot network transfer rates on a computer (for example, client, MediaAgent, or CommServe server).
After the additional settings are installed on the computer that you want to troubleshoot, send/receive throughput data is collected and recorded in the following file on that computer: <software_install_path>/Log Files/cvfwd.log.
The following image shows a sample data output from a cvfwd.log file:
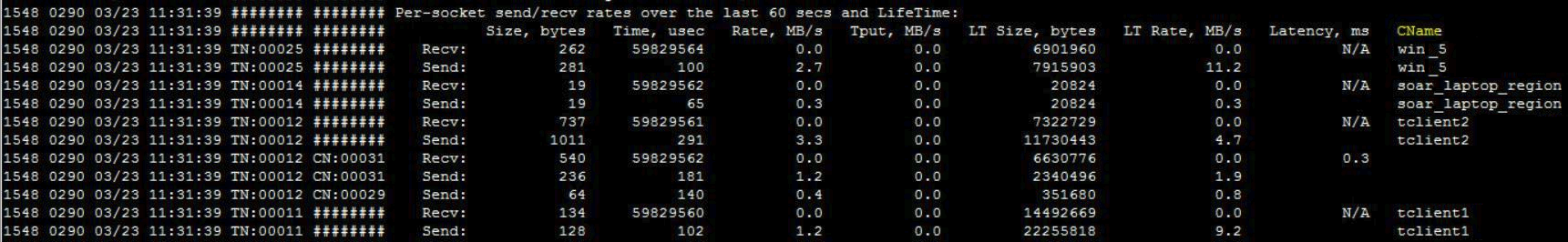
Where:
-
Size, bytes is the number of bytes that were sent/received during the last measuring interval.
-
LT Size, bytes is number of bytes that were sent/received over the socket's lifetime.
-
Time, usec is the effective time during which CVFWD was actively trying to send/receive data through this socket (in microseconds).
-
Rate, MB/s is the send/receive rates (that is, how fast CVFWD could send or receive data through this socket when it wanted to) during the last measuring interval. These numbers describe the actual speed of the media (that is, how fast the network can accept data queued in CVFWD, and how fast it can deliver pending data when CVFWD wants it.
-
LT Rate, MB/s is the send/receive rates over the socket's lifetime.
-
Tput, MB/s is the send/receive throughput (that is, how much data was sent or received during the last measuring interval rate). These numbers describe utilization of network bandwidth.
-
Latency, ms is the tunneling, valid for client sockets only (in milliseconds).
-
CName is the remote client name.
nSTATS_MEASURE_INTERVAL Additional Setting
This additional setting determines the interval (in seconds) that I/O statistics on a computer are measured.
To modify the value for the nSTATS_MEASURE_INTERVAL additional setting, follow the steps described in Adding or Modifying Additional Settings from the CommCell Console using the following parameters:
|
Name |
|
|
Category |
Firewall |
|
Type |
String |
|
Value |
0 to 60 (seconds) |
nSTATS_LOG_INTERVAL Additional Setting
This additional setting determines the interval (in seconds) that I/O statistics on a computer are logged.
To modify the value for the nSTATS_LOG_INTERVAL additional setting, follow the steps described in Adding or Modifying Additional Settings from the CommCell Console using the following parameters:
|
Name |
|
|
Category |
Firewall |
|
Type |
String |
|
Value |
0 to 86400 (seconds) |